They should identify potential shortfalls and recommend adjustments to keep your operations running smoothly. Monitor your liquidity ratio to ensure you can quickly convert assets into cash without losing value. A healthy ratio helps you avoid relying on emergency loans or credit lines for unexpected costs. Two funds might have the same returns, but their costs could be vastly different. A fund with a higher expense ratio might appear more attractive due to its past performance, but the higher fees could negate similar gains in the future. Carefully comparing expense ratios can help you maximize your long-term returns and achieve your financial goals.
Financial Close Solution
Advanced AI tools should analyze your financial data to uncover trends and opportunities. They should suggest strategies to improve payment terms, streamline operations, and optimize working capital, empowering you to make decisions that drive growth. Effective cash flow management tools should predict your financial position by forecasting incoming and outgoing cash.
Automated Debt Collection
A strong working capital ratio inspires confidence among investors and creditors. It demonstrates a company’s financial stability, reducing the perceived risk of default or cash flow issues. For publicly traded companies, this can positively impact stock prices and overall market perception. The net working capital to sales ratio, or working capital turnover ratio, is calculated by dividing sales revenue by working capital, which is derived from subtracting current liabilities from current assets. Working capital is calculated using the working capital formula, which subtracts current liabilities from current assets listed on the company balance sheet. The formula to calculate the working capital ratio divides a company’s current assets by its current liabilities.
- To fully understand your company’s performance, examining various metrics that shed light on differe…
- Because it excludes inventories and items that cannot be quickly converted into cash, the quick ratio gives a more realistic picture of a company’s ability to repay current obligations.
- It shows whether a company can breathe tomorrow morning or struggle to pay bills by Friday.
- If, say, you’re thinking about how to start a side hustle alongside your main enterprise, having cash ready lets you quickly jump on new opportunities.
- This is because growth typically requires investment in inventory and resources before bringing in additional cash, making your working capital cycle longer.
Free Cash Flow = Cash from Operations – CapEx

Such assets may come from ideas for second income streams such as creative ways to make money running in parallel to your main enterprise, and can help give your business a buffer to cover unexpected expenses. These are debts owed to your business through formal agreements and due within 12 months. Often arising from loans you’ve provided, these repayments can boost your cash reserves, helping to fund, say, low cost business ideas or simply adding a financial safety net. Another way to assess the situation is by looking at your working capital ratio, also known as the current ratio.
- One common financial ratio used to measure working capital is the current ratio, a metric designed to provide a measure of a company’s liquidity risk.
- You just need to subtract current liabilities from current assets to determine the available capital.
- Net working capital and working capitals often mean the same thing in practice.
- These measures the respective turnovers, e.g., days inventory outstanding means how many times the inventory was sold and replaced in a given year.
- Free cash flow is cash left after covering major expenses, while cash flow tracks all money moving in and out of the business.
- Here are a few working capital management tactics that you can use to improve your working capital, increase efficiencies, and ultimately improve earnings.
Expense ratios: What they are and why they matter
Seasonal working capital is the amount of money a business needs during its peak season. Businesses with seasonal demands require additional working capital, usually on a temporary basis when customer demand is high. Regular working capital is the minimum amount of capital required by a business to carry out its day-to-day operations. Net working capital is the difference between gross working capital and current liabilities. A higher ratio can offer the opportunity to invest in innovation and other initiatives that drive growth, potentially benefitting the company.
This financial metric shows how much cash and liquid assets a company has available to cover day-to-day expenses and short-term debts. The rapid increase in the amount of current assets indicates that the retail chain has probably gone through a fast expansion over the past few years and added both receivables and inventory. The sudden jump in current liabilities in the last year is particularly disturbing, and is indicative of the company https://i-devops.ir/estate-tax-internal-revenue-service-2/ suddenly being unable to pay its accounts payable, which have correspondingly ballooned.
- Current liabilities include trade payables, accrued liabilities, taxes payable, and the current portion of long-term debt.
- Since Walmart’s customers primarily make payments using cash, they have low accounts receivable, and excess cash on their books.
- On track for 90% automation by 2027, HighRadius is driving toward full finance autonomy.
- By maintaining a healthy balance between current assets and liabilities, businesses can ensure adequate liquidity, meet short-term obligations, and capitalize on growth opportunities.
- Working capital can be positive or negative, with a negative number potentially indicating financial risk like defaulting on debt payments—although there are some exceptions, which we’ll cover further on.
The working capital formula gives you an understanding of your cash-flow situation, ensuring you have enough money available to maintain the smooth running of your business. It’s also important for working capital ratio fueling growth and making your business more resilient. Knowing the difference between working capital and non-cash working capital is key to understanding the health of your cash flow and the liquidity of your current assets and obligations. Operating working capital, also known as OWC, helps you to understand the liquidity in your business. While net working capital looks at all the assets in your business minus liabilities, operating working capital looks at all assets minus cash, securities, and short-term, non-interest debts.
NTM EBITDA = NTM EBITDA Margin (%) × NTM Revenue

This distinction becomes even more valuable when ratios are monitored regularly, not just during closing cycles. Teams using modern tools like Farseer can calculate both ratios automatically from real-time actuals, updated inventory data, and live payables, without relying on Excel snapshots or static BI exports. This ensures that decisions are based on today’s numbers, not last week’s approximation.
Free Cash Flow (FCF) Formula
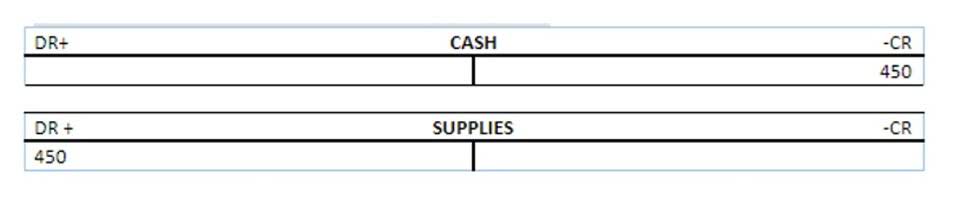
Non-cash working capital (NCWC) is the difference between current assets excluding cash and current liabilities. The ledger account working capital formula subtracts what a business owes from what it has to measure available funds for operations and growth. Inappropriate prepared plans of day-to-day expenses may result in enterprise liquidity issues. They have to postpone or arrange funds from some other sources, which give a bad impression of an enterprise on the party. Temporary working capital is capital that is required by the business during some specific times of the year or for some specific initiative.
- Working capital is the fund that the business needs to meet its daily expenses.
- For example, a retail business may experience increased sales during the holiday season, requiring additional working capital to manage inventory and meet customer demand.
- Buy enough inventory to fill customer orders but not so much that you deplete your bank account—less inventory leads to more cash flow that’s freed up.
- They allow faster responses to sudden opportunities or emergencies, financial obligations.
- The three sections of a cash flow statement under the indirect method are as follows.
- The working capital formula subtracts what a business owes from what it has to measure available funds for operations and growth.
- Generally speaking, a ratio of less than 1 can indicate future liquidity problems, while a ratio between 1.2 and 2 is considered ideal.
Types of Free Cash Flow
Explore the benefits of discounted cash flow calculations and elevate your business investment strategy. Additionally, exploring additional sales channels or attending small business networking events can widen your market reach, leading to improved liquidity and ensuring you have cash available when needed. Sometimes, working capital looks good on paper but doesn’t tell you if you can access cash when you really need it. Let’s imagine you’ve explored how to start a business from home and have decided upon selling rare and collectible books online. Holding more stock can increase the value of current assets, but it’s certainly possible to have too much of a good thing. Items can become outdated or even get stolen, which means your working capital might not be as strong as you think.
